- Home >> Latest News
Hyperconnectivity in perisylvian language pathways in schizophrenia with auditory verbal hallucinations: A multi-site diffusion MRI study
Sangma Xie a, Bing Liu b,c,d,e, Jiaojian Wang f, Yuan Zhoug h, Yue Cui b,c,d, Ming Song b,c,d, Yunchun Chen i, Peng Li j,k, Lin Lu j,k, Luxian Lv l,m, Huaning Wang i, Hao Yan j,k, Jun Yan j,k, Hongxing Zhang l,n,Dai Zhang j,k,o, Tianzi Jiang b,c,d,e,f,.
a College of Life Information Science and Instrument Engineering, Hangzhou Dianzi University, Hangzhou 310018, China
b Brainnetome Center, Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China
c National Laboratory of Pattern Recognition, Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China
d University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China
e CAS Center for Excellence in Brain Science and Intelligence Technology, Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China
f Key Laboratory for NeuroInformation of Ministry of Education, School of Life Science and Technology, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu 610054, China
g Key Laboratory of Behavioral Science, Institute of Psychology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China
h Magnetic Resonance Imaging Research Center, Institute of Psychology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China
i Department of Psychiatry, Xijing Hospital, The Fourth Military Medical University, Xi'an 710032, China
j Peking University Sixth Hospital/Institute of Mental Health, Beijing 100191, China
k Key Laboratory of Mental Health, Ministry of Health (Peking University), Beijing 100191, China
l Department of Psychiatry, Henan Mental Hospital, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Xinxiang Medical University, Xinxiang 453002, China
m Henan Key Lab of Biological Psychiatry, Xinxiang Medical University, Xinxiang 453002, China
n Department of Psychology, Xinxiang Medical University, Xinxiang 453002, China
o Center for Life Sciences/PKU-IDG/McGovern Institute for Brain Research, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
Abstract:
Auditory verbal hallucinations (AVH) are one of the cardinal symptoms of schizophrenia, and are proposed to be associatedwith altered integrity of the left perisylvian language pathways. There is considerable heterogeneity in the pattern of white matter abnormalities across previous studies. We investigated the white matter integrity of the perisylvian language pathways in schizophrenia patients with AVH based on a relatively large sample dataset fromfour different sites. 113 schizophrenia patientswith AVH, 96 patientswithout AVH(nAVH), and 269 healthy controls (HC) underwent diffusion-weighted imaging. Between-group comparisonswere performed on the fractional anisotropy (FA) values of the anterior, posterior, and long segment fasciculi within the perisylvian language network. Analysis of covariance among the 3 groups revealed the long segment of the left perisylvian language pathways was significantly different in FA value. Post hoc analysis showed that compared with the HC group, the AVH group had significantly higher FA measurements in the left long segment. The nAVH group showed intermediate FA values for this segment compared to the AVH and HC group but did not differ significantly from either group. Furthermore, the prospective meta-analyses also revealed that FA value of the left long segment was significantly higher in the AVH group compared to the HC group. Our findings suggest the hyperconnectivity pattern of the left perisylvian language pathways in the presence of AVH in schizophrenia and support the self-monitoring of inner speech model.
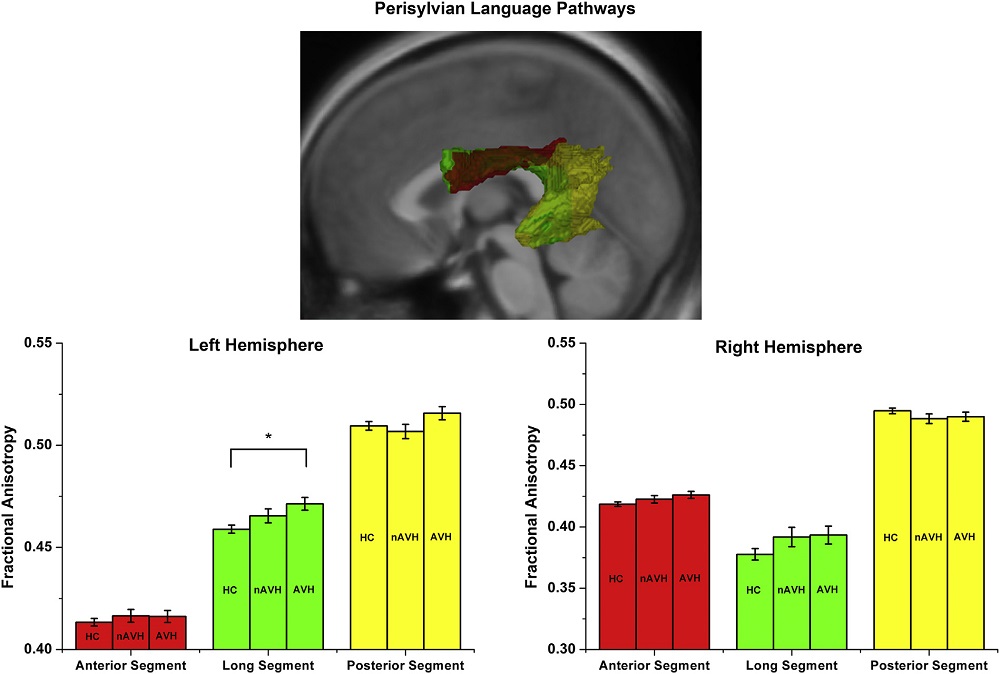
Fig. 1. Differences in FA value between healthy controls (HC), schizophrenia patients without auditory verbal hallucinations (nAVH), and schizophrenia patients with auditory verbal hallucinations (AVH) in the anterior, long, and posterior segments of the perisylvian language network for the combined dataset. The asterisk (*) indicates a statistically significant difference at P < 0.05 with Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons. Error bars indicate standard errors.
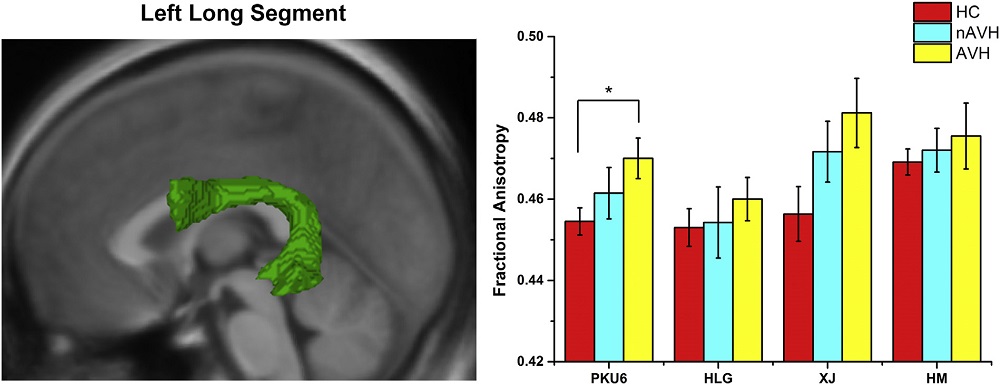
Fig. 2. Differences in FA value between healthy controls (HC), schizophrenia patients without auditory verbal hallucinations (nAVH), and schizophrenia patients with auditory verbal hallucinations (AVH) in the long segment of the left perisylvian language network for each site (PKU6, HLG, XJ and HM). The asterisk (*) indicates a statistically significant difference at P < 0.05 with Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons. Error bars indicate standard errors.
